What is Amazon Business?
Amazon Business refers to how entrepreneurs and companies can leverage Amazon’s vast e-commerce platform to sell products or services. With over 310 million active customers worldwide, [Source: Amzscout] Amazon provides a massive marketplace with opportunities for businesses of all sizes to thrive. From private label sellers to wholesale distributors, Amazon offers different business models tailored to varying goals and resources.
Amazon Business Models For Sellers: Types, Explanations, and Examples
Amazon provides several business models, each with unique features and requirements. Below, we break down the primary models:
1. Private Label
Private Labeling involves creating your brand and selling products manufactured by you or a third party under your label. This model allows sellers to control product branding and pricing, potentially leading to higher profit margins.
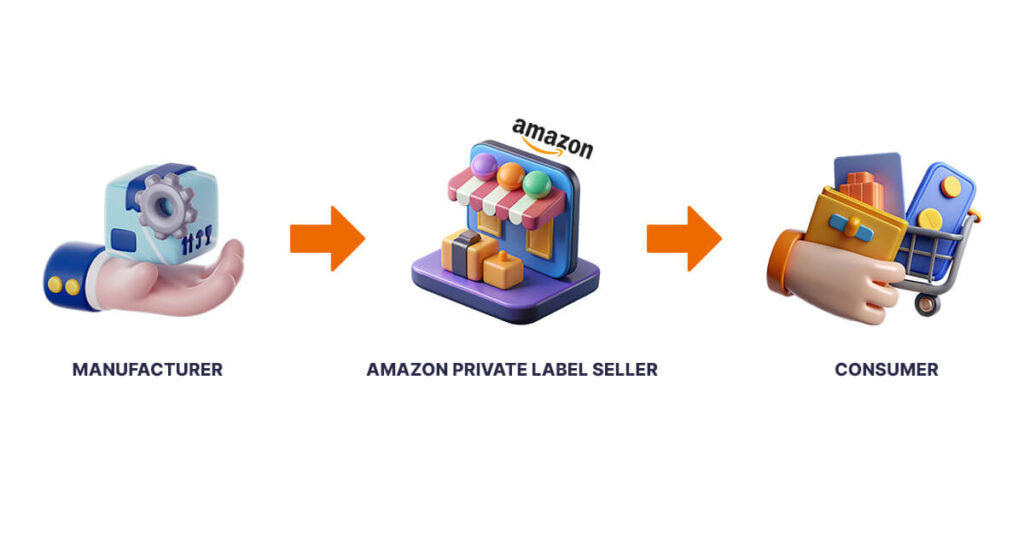
Example: A company sourcing stainless steel water bottles from a manufacturer, branding them with a unique logo, and selling them on Amazon.
Pros:
- High-profit margins.
- Full control over branding.
- Long-term business growth.
Cons:
- Requires significant upfront investment.
- High competition.
- Longer time to market.
2. Wholesale Arbitrage
The Wholesale arbitrage model involves purchasing bulk products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted prices and selling them on Amazon for a profit. Unlike Private labels, wholesale arbitrage sellers sell established brands.
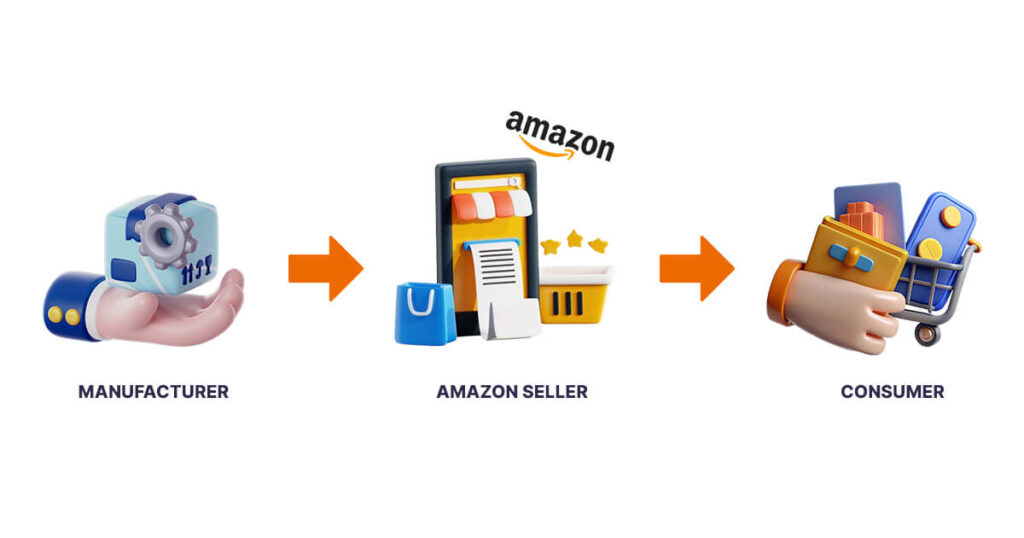
Example: A business buying electronics from Sony at wholesale prices and reselling them on Amazon.
Pros:
- Established brand recognition.
- Lower marketing costs.
- Faster sales cycles.
Cons:
- Lower profit margins.
- Dependency on suppliers.
- Intense competition.
3. Retail Arbitrage
Retail Arbitrage involves buying discounted or clearance items from retail stores and reselling them on Amazon at a higher price.
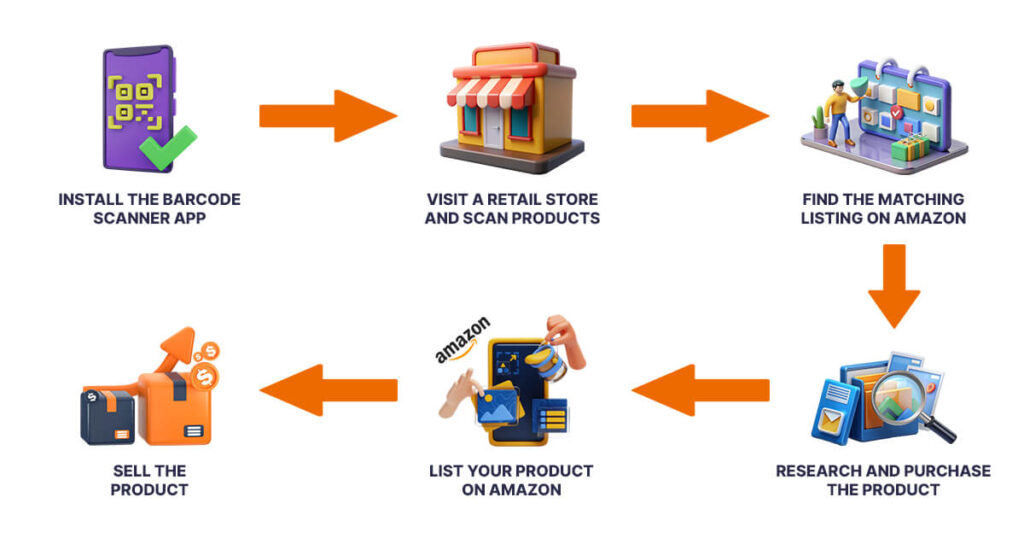
Example: Purchasing discounted toys from Walmart and selling them on Amazon during the holiday season.
Pros:
- Low upfront cost.
- Quick turnaround.
- Easy to start.
Cons:
- Inconsistent product availability.
- Lower scalability.
- Possible legal issues with brand restrictions.
4. Online Arbitrage
Similar to Retail Arbitrage, products are sourced online instead of in physical retail stores.
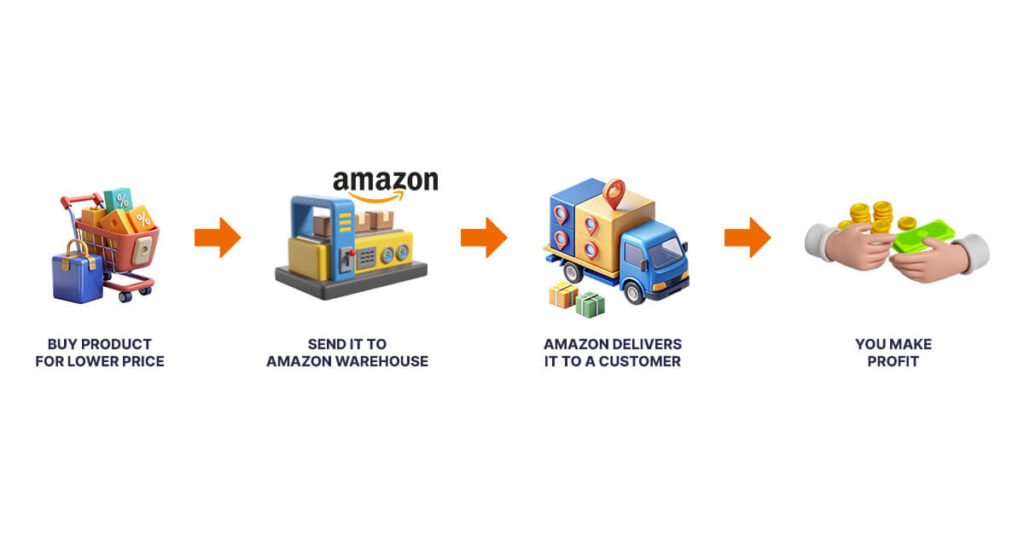
For example, find a discounted product on eBay and resell it on Amazon for a profit.
Pros:
- Flexible sourcing.
- No physical store visits are required.
- Potentially higher profit margins than Retail Arbitrage.
Cons:
- Requires constant price monitoring.
- Risk of buying counterfeit products.
- High competition.
5. Dropshipping
Dropshipping involves listing products on Amazon without holding inventory. When a sale is made, the order is fulfilled by a third-party supplier who ships the product directly to the customer.
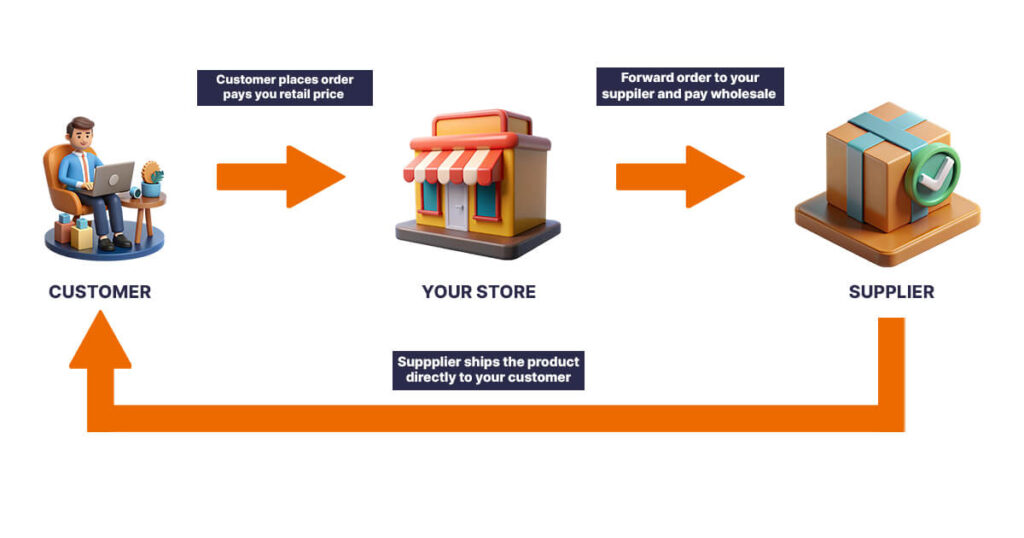
Example: Listing home decor items on Amazon, and when a sale occurs, the supplier ships the item directly to the customer.
Pros:
- No need for inventory storage.
- Low startup costs.
- Wide range of products.
Cons:
- Low-profit margins.
- Limited control over product quality and shipping.
- High competition.
6. Handmade
Amazon Handmade is for artisans and crafters who create handmade products. This model is ideal for those who want to sell unique, handcrafted items on a global platform.
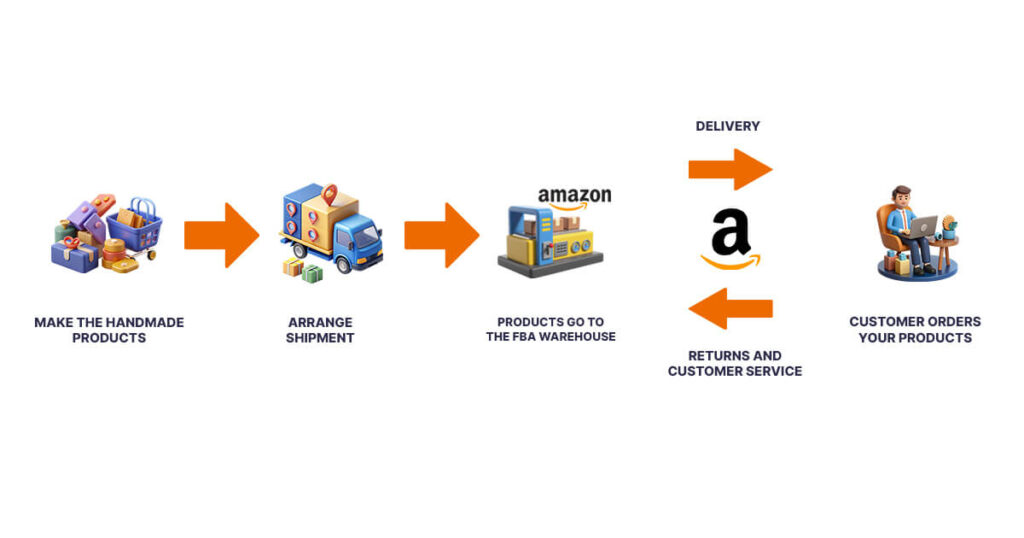
Example: Selling custom-made jewelry or hand-knitted scarves.
Pros:
- Niche market.
- Control over pricing.
- Support for small businesses.
Cons:
- Limited scalability.
- Time-consuming production process.
- Higher fees than other models.
Comparison Table of Amazon Business Models
| Business Model | Upfront Cost | Profit Margin | Scalability | Control | Competition |
| Private Label | High | High | High | Full | High |
| Wholesale | Medium | Medium | Medium | Low | High |
| Retail Arbitrage | Low | Low | Low | Medium | High |
| Online Arbitrage | Low | Low | Low | Medium | High |
| Dropshipping | Low | Low | Medium | Low | High |
| Handmade | Low | Medium | Low | Full | Low |
How to Start Selling on Amazon
1. Choose a Business Model
The first step in exploring Amazon Business Models is selecting one that aligns with your goals, budget, and resources. For those looking to build a brand, the Private Label model may be the best choice. If you prefer a lower-risk approach, Retail or Online Arbitrage could be ideal.
2. Set Up Your Business
To start selling, you’ll need to set up your Amazon Seller account and establish your business legally:
- Amazon Seller Account: You can choose between an Individual Plan ($0.99 per item sold) or a Professional Plan ($39.99 per month), depending on your expected sales volume. You’ll need to provide details like your business name, legal name, contact information, and shipping details.
- Business Structure: Decide whether you want to operate as a sole proprietorship, LLC, or another legal entity. Forming an LLC is often recommended as it provides liability protection and can offer tax benefits.
- Permits and Licenses: Depending on your location and the products you plan to sell, you may need specific business licenses and permits.
3. Source Your Products
Once your business is set up, you need to source products to sell:
- Private Label/Wholesale: Source products from manufacturers or distributors. Alibaba is a popular platform for finding suppliers, but it’s essential to verify their credibility.
- Arbitrage: Identify products with high demand and low competition in local retail stores or online marketplaces.
- Dropshipping: Partner with a reliable supplier who can fulfill orders on your behalf.
4. Create Product Listings
After sourcing your products, you’ll need to create product listings on Amazon:
- Optimized Listings: Include high-quality images, detailed descriptions, and relevant keywords to improve visibility and attract customers.
- Pricing Strategy: Set competitive prices, considering Amazon fees and your desired profit margins.
5. Manage Inventory and Orders
Depending on your chosen business model from Amazon Business Models, you’ll either manage inventory yourself or use Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) service:
- FBA: Amazon handles storage, shipping, and customer service, allowing you to focus on growing your business.
- FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant): If you choose to handle shipping, you’ll need to manage inventory and orders manually.
6. Market Your Products
To drive sales, you’ll need to invest in marketing:
- Amazon Advertising: Utilize Amazon’s PPC (Pay-Per-Click) ads to promote your products.
- Social Media: Leverage social media platforms to build brand awareness and drive traffic to your listings.
- SEO: Optimize your product listings for search engines to improve organic visibility.
Which Business Model to Choose?
Your choice of business model depends on your resources, experience, and long-term goals. Here are some considerations for selecting the right one from Amazon Business Models:
- If you have a strong interest in branding: Private Label is the best option.
- If you want to sell established products with less branding effort: Wholesale Arbitrage is ideal.
- If you have limited capital: Retail or Online Arbitrage offers low-risk entry points.
- If you want to avoid inventory management: Dropshipping or Amazon FBA is suitable.
- If you are an artisan: Amazon Handmade is a niche but rewarding option.
The Importance of Forming an LLC for Amazon Business
Forming a Limited Liability Company (LLC) for your Amazon business is crucial for several reasons:
- Legal Protection: An LLC separates your assets from your business liabilities, protecting you in case of lawsuits or debt.
- Tax Benefits: LLCs offer flexible tax options, allowing you to choose how you’re taxed (as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation).
- Professional Credibility: Having an LLC can enhance your business’s credibility with customers, suppliers, and investors.
Rocket Wave offers comprehensive services to help entrepreneurs establish their LLCs. Our team assists with:
- LLC Formation: We guide you through the process of forming an LLC, ensuring all legal requirements are met.
- EIN/ITIN Application: We assist with obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), necessary for tax filings.
- Tax Compliance: Our experts help you navigate tax laws to ensure your Amazon business remains compliant.
By registering with Rocket Wave, you can focus on growing your Amazon business while we handle the legal and administrative details.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to Amazon seller business models, how to start selling, and the importance of forming an LLC. With the right approach, you can build a successful Amazon business and benefit from the support offered by Rocket Wave.





